

This may be particularly severe after previous surgical compromise of the coracoacromial arch.

Chronic massive cuff defects may present with anterosuperior instability of the humeral head on attempted elevation of the arm.
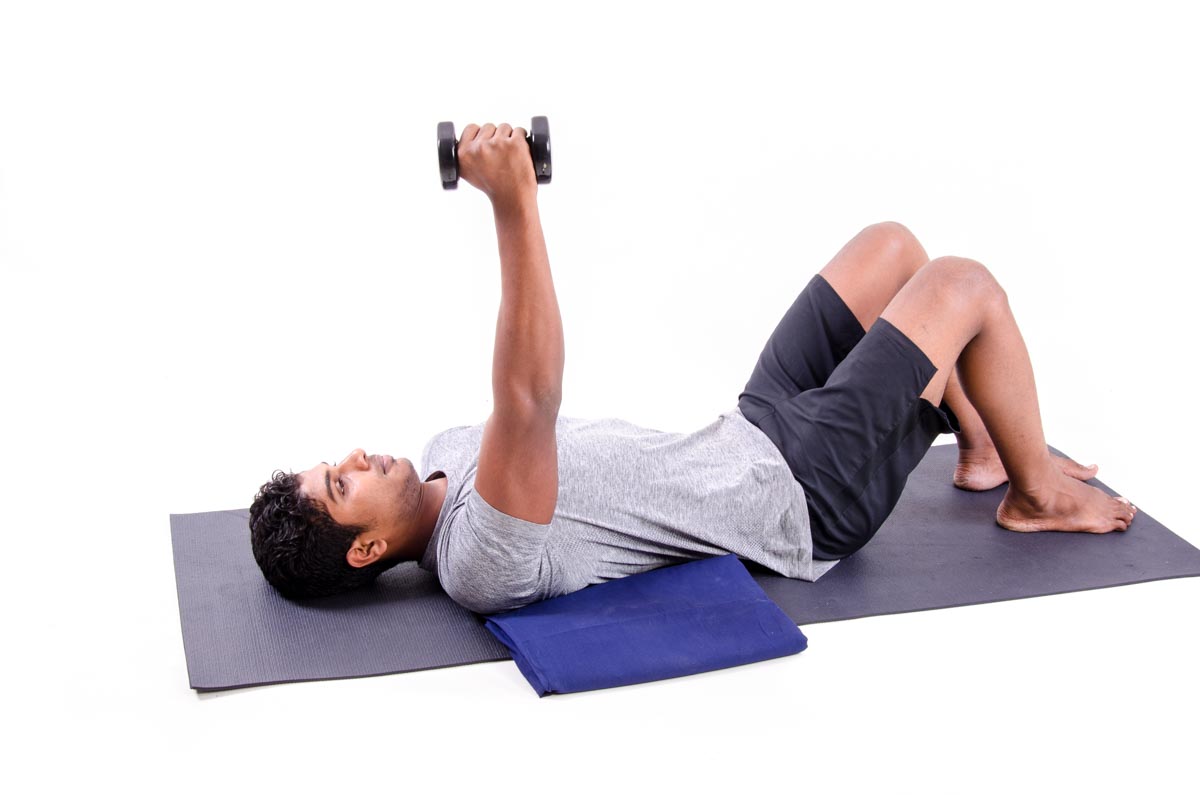

A boutonniere deformity is evident when no cuff can be palpated over the humeral head. Crepitance on rotation of the arm elevated to shoulder height may result from the abrasion of torn tendon margins against the coracoacromial arch a positive "abrasion sign". The defect is usually just posterior to the bicipital groove and medial to the greater tuberosity. Defects in the cuff can often be palpated by rotating the proximal humerus under the examiner's finger placed at the anterior corner of the acromion. Rupture of the long head of the biceps is frequently evident on inspection of shoulders with rotator cuff tears. Subtle atrophy can be seen most easily by casting a shadow from a light over the head of the patient. The surgeon can also determine preoperatively the patient's goals and functional expectations for surgical treatment to see whether these are reasonable in view of the likely prognosis.Ĭhronic rotator cuff tears are accompanied by atrophy of the spinatus muscles. The prognosis for a durable repair is even worse if the history reveals local or systemic steroids smoking or difficulties in healing previous injuries or surgeries. Long-standing tears associated with major weakness in older patients carry a poor prognosis. Acute tears in younger healthy individuals without prior shoulder disease are likely to be repairable. Substantial information bearing on the reparability of a rotator cuff defect can also be determined from the history. It is evident that sleeping on the affected side placing the hand behind the head lifting eight pounds and throwing overhand are particularly compromised by cuff tears. The Simple Shoulder Test provides a set of data for characterizing some functional impairment from rotator cuff tears. Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy is suggested by the atraumatic onset of bilateral symmetrical weakness of the scapular musculature. suprascapular neuropathy from compression/entrapment: insidious onset of external rotator weakness.suprascapular neuropathy from traction: external rotation weakness following an injury in which the shoulder was forced down and the neck forced to the opposite side (may be part of a full Erb's palsy) and.suprascapular neuropathy from brachial neuritis: acute onset of pain lasting several weeks followed by profound weakness of external rotation.
cervical radiculopathy: pain on top of the shoulder with radiation down the arm below the deltoid tubercle weakness of the biceps diminished biceps reflex and sensory changes on the lateral forearm.long thoracic nerve palsy: posterior protrusion of the scapula on attempts to elevate the arm.These traumatic cuff tears may also involve the subscapularis producing weakness in internal rotation.Ĭharacteristic elements of the history of other common causes of shoulder weakness include: Traumatic glenohumeral dislocations in individuals over the age of 40 have a strong association with rotator cuff tears. A history of sudden eccentric loading such as trying to support a falling load or trying to cushion a fall with the arm is commonly given by younger patients with cuff tears. More acute incremental losses of strength from tear propagation may follow lifting or falls.Ī greater injury is required to tear the cuff of individuals at the younger end of the age distribution. The shoulder may have been treated with steroid injections with some relief of discomfort but without improvement in strength. There is a typical age distribution of patients presenting for evaluation of full thickness rotator cuff defects.Ī typical history for degenerative cuff fiber failure in an older individual reveals an insidious onset of weakness of flexion and external rotation perhaps punctuated by episodes of "bursitis" or "tendonitis." Failure of weakened tendon tissue may not produce much in the way of pain bleeding or swelling. Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine Bulletin.Resident Research - Intake and Travel Award Forms.Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine Interest Group.Residents Portal and Digital Curriculum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
